GLP-1 medications have revolutionized the management of type 2 diabetes and weight loss. These medications work by mimicking a natural hormone that regulates blood sugar levels and appetite, making them an effective treatment option.
Understanding GLP-1 time to onset is crucial for individuals starting this treatment, as it helps set realistic expectations for their journey towards better health.
By knowing what to expect, individuals can better adhere to their treatment plan and achieve their health goals.
Key Takeaways
- GLP-1 medications are used for managing type 2 diabetes and weight loss.
- They work by mimicking a natural hormone that regulates blood sugar and appetite.
- Understanding the onset time of GLP-1 medications is crucial for treatment adherence.
- GLP-1 medications can help individuals achieve their health goals.
- Knowing what to expect from GLP-1 treatment can improve patient outcomes.
Understanding GLP-1 Medications
GLP-1 receptor agonists are a relatively new class of medications that mimic a natural hormone involved in glucose regulation. These medications have shown significant promise in treating type 2 diabetes and weight management by leveraging the body’s natural processes.
What Are GLP-1 Receptor Agonists?
GLP-1 receptor agonists are drugs that mimic the action of the incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), which is involved in glucose metabolism and appetite regulation. By activating GLP-1 receptors, these medications enhance insulin secretion, suppress glucagon release, and slow gastric emptying, thereby improving glycemic control.
Common GLP-1 Medications on the Market
Several GLP-1 receptor agonists are available on the market, including semaglutide (Ozempic, Wegovy) and tirzepatide (Mounjaro). These medications are administered via injection and are known for their efficacy in managing type 2 diabetes and, in some cases, obesity.
| Medication | Brand Name | Primary Use |
|---|---|---|
| Semaglutide | Ozempic, Wegovy | Type 2 Diabetes, Weight Management |
| Tirzepatide | Mounjaro | Type 2 Diabetes |
FDA-Approved Uses for GLP-1 Medications
GLP-1 receptor agonists have been approved by the FDA for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and, in some cases, for weight management in obese patients. Their ability to improve glycemic control and promote weight loss has made them a valuable treatment option for many patients.
Key Benefits: Improved glycemic control, weight loss, reduced risk of major adverse cardiovascular events.
The Science Behind GLP-1 Medications
Understanding GLP-1 medications requires a look into the hormone they mimic and how it functions within the body. GLP-1, or Glucagon-Like Peptide-1, is an incretin hormone that plays a crucial role in glucose metabolism. It is naturally released in response to food intake and helps regulate blood sugar levels.
Natural GLP-1 in the Body
Natural GLP-1 is secreted by the intestines in response to nutrient ingestion. It stimulates insulin secretion while suppressing glucagon release, thereby lowering blood glucose levels. This hormone also influences gastric emptying and has been shown to affect appetite and satiety centers in the brain.
How Synthetic GLP-1 Medications Differ
Synthetic GLP-1 receptor agonists are designed to mimic the action of natural GLP-1 but with a longer duration of action. These medications resist rapid degradation by dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4), allowing them to remain active in the body for a longer period.
Target Receptors and Biological Pathways
GLP-1 medications target GLP-1 receptors found in various tissues, including the pancreas, heart, and brain. By activating these receptors, they enhance glucose-dependent insulin secretion, suppress glucagon release, and influence other metabolic processes.
The pharmacokinetics of GLP-1 medications vary, with some having a more rapid onset and others a longer duration of action. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the most appropriate treatment for individual patient needs.
How Long Does It Take for GLP-1 to Work?
The effectiveness of GLP-1 receptor agonists is well-documented, but the timeframe for noticing improvements can vary based on several factors. GLP-1 medications are used to treat type 2 diabetes and obesity, and their onset of action can differ from person to person.
Initial Effects Timeline
Some individuals may experience the initial effects of GLP-1 medications within a few days to a few weeks after starting treatment. These early effects can include improvements in blood glucose levels and reduced appetite. For instance, a study on semaglutide, a popular GLP-1 receptor agonist, showed significant reductions in HbA1c levels within the first few weeks of treatment.
Full Therapeutic Effect Timeline
The full therapeutic effect of GLP-1 medications typically becomes apparent after several weeks to a few months. For example, maximum weight loss benefits may take up to 6 months or more to achieve. It’s essential for patients to be patient and adhere to their prescribed treatment regimen to maximize the benefits of GLP-1 therapy.
Factors Affecting Response Time
Several factors can influence how quickly an individual responds to GLP-1 medications. These include:
- Dosage: Higher doses may lead to faster results, but may also increase the risk of side effects.
- Individual health: Patients with certain health conditions or comorbidities may respond differently to GLP-1 therapy.
- Lifestyle factors: Diet, exercise, and other lifestyle habits can impact the effectiveness of GLP-1 medications.
For a comprehensive comparison of different GLP-1 medications, such as tirzepatide and semaglutide, visit this resource for more information.
Individual Variation in Response
It’s crucial to recognize that individual responses to GLP-1 medications can vary significantly. While some may experience rapid improvements, others may take longer to notice benefits. Regular monitoring and adjustments to treatment plans can help optimize outcomes.
GLP-1 Mechanism of Action Explained
The mechanism of action of GLP-1 receptor agonists is multifaceted, involving several key physiological processes. GLP-1 medications work by mimicking the action of the naturally occurring GLP-1 hormone in the body, which plays a crucial role in glucose metabolism and appetite regulation.
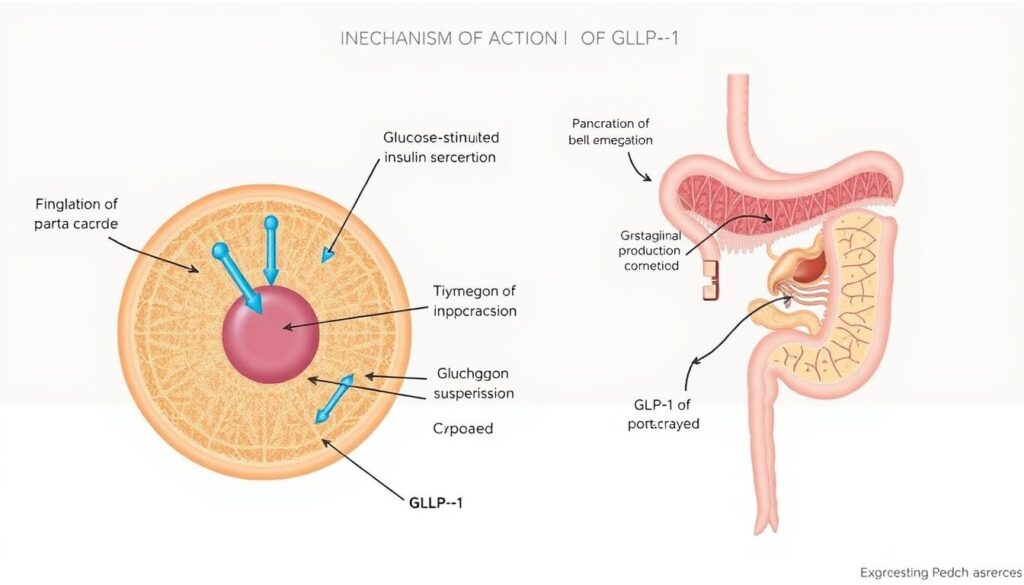
Effects on Insulin Production
One of the primary actions of GLP-1 receptor agonists is to stimulate insulin secretion in a glucose-dependent manner. This means that they enhance the release of insulin from the pancreas when blood glucose levels are high, thereby helping to lower blood sugar. This effect is particularly beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes, as it improves glycemic control without significantly increasing the risk of hypoglycemia.
Impact on Glucagon Secretion
GLP-1 medications also suppress the secretion of glucagon, a hormone that raises blood glucose levels. By reducing glucagon levels, GLP-1 receptor agonists further contribute to lowering blood glucose. This dual action on insulin and glucagon helps to achieve better glycemic control.
Influence on Gastric Emptying
Another important effect of GLP-1 receptor agonists is their ability to slow gastric emptying. This delay in the movement of food from the stomach to the small intestine helps to reduce postprandial (after meal) glucose spikes. Slower gastric emptying also contributes to feelings of fullness and satisfaction, which can aid in weight management.
Brain Signaling and Appetite Regulation
GLP-1 receptor agonists influence appetite regulation through brain signaling. They act on the hypothalamus, the part of the brain that controls hunger and satiety, leading to reduced appetite and food intake. This effect is particularly beneficial for weight loss in individuals with obesity.
In summary, the GLP-1 mechanism of action is complex and involves multiple physiological pathways. By stimulating insulin secretion, suppressing glucagon release, slowing gastric emptying, and regulating appetite, GLP-1 receptor agonists provide a comprehensive approach to managing type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Ozempic (Semaglutide): Effectiveness Timeline
Semaglutide, marketed under the brand name Ozempic, is a significant advancement in the treatment of type 2 diabetes, providing improved glycemic control and weight management. Ozempic is administered via injection once a week and has been shown to be effective in clinical trials for improving blood sugar control and promoting weight loss.
Initial Blood Sugar Effects
Patients typically start noticing improvements in their blood sugar levels within the first few weeks of starting Ozempic. Studies have shown that semaglutide can significantly reduce HbA1c levels, a measure of average blood glucose over the past 2-3 months, within the first 4-6 weeks of treatment.
Weight Loss Timeline
Weight loss with Ozempic is progressive, with noticeable reductions often reported within the first 12 weeks. Clinical trials have demonstrated that patients can achieve substantial weight loss, with some losing up to 10% or more of their initial body weight over the course of several months.

Dosing Schedule and Titration
Ozempic is initiated at a dose of 0.25 mg once weekly for the first four weeks, after which the dose is increased to 0.5 mg once weekly. For patients requiring further glycemic control, the dose can be titrated up to 1 mg once weekly. This gradual titration helps minimize gastrointestinal side effects.
Real Patient Experiences
Many patients have reported not only improved blood sugar control but also significant weight loss and reduced appetite. For instance, a patient might say, “Since starting Ozempic, I’ve noticed a significant decrease in my blood sugar levels and I’ve lost a considerable amount of weight, which has greatly improved my overall health and well-being.”
In conclusion, Ozempic (semaglutide) offers a comprehensive approach to managing type 2 diabetes, with benefits extending beyond glycemic control to include weight management. Its effectiveness timeline varies among individuals, but most patients experience noticeable improvements within the first few weeks to months of treatment.
Wegovy (Semaglutide for Weight Management): Results Timeline
Wegovy, with its active ingredient semaglutide, is revolutionizing weight loss journeys by providing a clinically-backed solution. As a formulation specifically approved for weight management, Wegovy has shown significant promise in clinical trials, offering new hope for individuals struggling with weight loss.

Expected Weight Loss by Week
Clinical trials have demonstrated that patients on Wegovy can expect substantial weight loss. Typically, weight loss is noticeable within the first few weeks of starting treatment. On average, participants in clinical trials experienced a significant reduction in body weight within the initial 4-8 weeks.
Plateau Periods and How to Overcome Them
As with any weight loss regimen, plateau periods are common. These are periods where weight loss slows down or appears to stop. To overcome plateaus, it’s recommended to review and adjust dietary habits and ensure consistent adherence to the prescribed Wegovy dosing schedule.
Maximum Effectiveness Timeline
The maximum effectiveness of Wegovy is typically observed after around 20 weeks of treatment. However, individual results can vary, and some may experience continued weight loss beyond this point.
Maintenance Phase Expectations
Once the desired weight loss is achieved, the focus shifts to maintaining the weight loss. Continued use of Wegovy as prescribed, along with sustainable lifestyle changes, is crucial for maintaining weight loss over the long term.
Understanding the timeline for Wegovy’s effectiveness is key to managing expectations and achieving successful weight loss outcomes. By combining Wegovy with healthy lifestyle choices, individuals can maximize their weight loss journey.
Mounjaro (Tirzepatide): Dual GIP/GLP-1 Timeline
As a dual GIP/GLP-1 receptor agonist, Mounjaro offers a novel approach to managing both blood glucose levels and weight. This innovative medication has shown promising results in clinical trials, particularly in its ability to address both diabetes management and weight loss simultaneously.
Unique Mechanism of Action
Mounjaro works by targeting two key hormone receptors: GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide) and GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1). This dual action enhances its effectiveness in improving glycemic control and promoting weight loss. The medication’s unique mechanism of action sets it apart from other GLP-1 receptor agonists on the market.
Comparative Speed of Results
Clinical trials have shown that Mounjaro can produce significant results relatively quickly. Patients typically begin to see improvements in their blood glucose levels within the first few weeks of treatment.
| Treatment Week | Average HbA1c Reduction | Average Weight Loss |
|---|---|---|
| 4 weeks | 0.5% | 2 kg |
| 12 weeks | 1.2% | 5 kg |
| 24 weeks | 2.0% | 8 kg |
Diabetes Management Timeline
Mounjaro has demonstrated a significant impact on diabetes management. Patients can expect to see improvements in their HbA1c levels within the first 12 weeks, with continued improvement up to 24 weeks and beyond.
Weight Loss Progression
In addition to its effects on blood glucose, Mounjaro has been shown to promote substantial weight loss. The weight loss progression is typically gradual, with noticeable reductions within the first 12 weeks and continued loss up to 24 weeks.
Mounjaro’s dual GIP/GLP-1 agonist activity makes it a valuable option for patients struggling with both type 2 diabetes and obesity. As with any medication, individual results may vary, and patients should consult their healthcare provider for personalized guidance on the glp-1 therapy timeline.

Short-Acting vs. Long-Acting GLP-1 Medications
GLP-1 medications come in various formulations, each with its unique duration of action. This variation allows healthcare providers to tailor treatment to individual patient needs and preferences. Understanding the differences between short-acting and long-acting GLP-1 medications is crucial for making informed decisions about diabetes management and weight loss treatment.
Byetta and Adlyxin: Rapid Onset Profiles
Short-acting GLP-1 receptor agonists like Byetta (exenatide) and Adlyxin (lixisenatide) have a rapid onset of action. Byetta, for instance, is administered twice daily and is known for its ability to improve postprandial glucose control. These medications are particularly effective in reducing glucose spikes after meals.
Trulicity, Victoza, and Bydureon: Extended Action
Long-acting GLP-1 medications, such as Trulicity (dulaglutide), Victoza (liraglutide), and Bydureon (exenatide extended-release), offer extended action, allowing for less frequent dosing. Trulicity, for example, is administered once weekly and provides sustained GLP-1 receptor activation, leading to improved glycemic control and weight management.
Choosing Between Daily and Weekly Options
The choice between daily and weekly GLP-1 medications depends on several factors, including patient preference, dosing frequency, and individual response to treatment.
“The flexibility in dosing options allows healthcare providers to personalize treatment plans, enhancing patient adherence and outcomes.”
When deciding between short-acting and long-acting GLP-1 medications, it’s essential to consider the patient’s lifestyle, treatment goals, and potential side effects.
GLP-1 for Diabetes Management: Timeline of Effects
GLP-1 medications provide a multifaceted approach to diabetes management, impacting not just blood glucose levels but also weight and overall glycemic control. For individuals with type 2 diabetes, understanding the timeline of GLP-1 medication effects is crucial for managing expectations and optimizing treatment plans.
Blood Glucose Improvements
One of the primary benefits of GLP-1 receptor agonists is their ability to improve blood glucose control. Significant reductions in blood glucose levels can be observed within the first few weeks of treatment. Studies have shown that GLP-1 medications can decrease fasting plasma glucose by up to 30 mg/dL, providing a substantial improvement in glycemic control.
HbA1c Reduction Timeline
HbA1c levels are a critical marker for long-term blood glucose control. GLP-1 medications have been shown to reduce HbA1c levels by an average of 1-2% over a period of 12-26 weeks. The timeline for HbA1c reduction can vary depending on the specific medication, dosing schedule, and individual patient factors.
Long-Term Glycemic Control
Beyond initial improvements, GLP-1 medications offer sustained long-term glycemic control. Continuous use of GLP-1 receptor agonists has been associated with maintained reductions in HbA1c levels and improved overall diabetes management. This long-term control is crucial for reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications.
By understanding the timeline of GLP-1 medication effects, healthcare providers and patients can better navigate the treatment process, making informed decisions to achieve optimal diabetes management.
GLP-1 for Weight Management: When to Expect Results
When using GLP-1 receptor agonists for weight loss, it’s essential to understand the timeline for expected results. GLP-1 medications can lead to significant weight loss, but individual results may vary.
Initial Weight Loss Timeline
The initial weight loss timeline for GLP-1 medications can be quite encouraging. Most people start to notice weight loss within the first few weeks of treatment. Studies have shown that significant weight loss can occur within the first 12 weeks.
Plateau Periods and Continued Progress
As with any weight loss program, plateau periods can occur. However, continuing the medication and making lifestyle adjustments can help overcome these plateaus. It’s essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to adjust the treatment plan as needed.
Understanding that weight loss is not always linear is crucial. Some people may experience a slower rate of weight loss after the initial period, but this doesn’t mean the medication is not working.
Maximum Weight Loss Expectations
The maximum weight loss expectations for GLP-1 medications vary among individuals. Clinical trials have shown that some people can achieve up to 15-20% weight loss when using these medications in conjunction with diet and exercise.
Maintaining Results Long-Term
Maintaining weight loss results long-term requires continued use of the medication and commitment to lifestyle changes. A healthy diet and regular physical activity are crucial for sustaining weight loss over time. Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider can also help in making necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
Side Effects: When They Appear and How Long They Last
Understanding the potential side effects of GLP-1 medications is crucial for patients to navigate their treatment effectively. GLP-1 receptor agonists have been associated with various side effects, ranging from mild to severe.
Common Initial Side Effects
When initiating GLP-1 therapy, patients often experience gastrointestinal side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. These symptoms are usually most pronounced in the first few weeks of treatment.
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
Side Effects That Diminish Over Time
Many patients find that the initial side effects diminish over time as their body adjusts to the medication. However, the rate at which this occurs can vary significantly among individuals.
Persistent Side Effects to Monitor
While some side effects may decrease, others can persist. It’s essential for patients to monitor their condition and report any persistent or severe side effects to their healthcare provider.
| Side Effect | Action |
|---|---|
| Persistent nausea | Consult healthcare provider for dosage adjustment |
| Severe abdominal pain | Seek immediate medical attention |
Managing Side Effects Effectively
Managing side effects effectively is key to maintaining adherence to GLP-1 therapy. Strategies include dietary adjustments, taking the medication at the right time, and, in some cases, adjusting the dosage.
By understanding the potential side effects and how to manage them, patients can maximize the benefits of their GLP-1 medication while minimizing its drawbacks.
Maximizing GLP-1 Effectiveness
To maximize the benefits of GLP-1 medications, it’s crucial to adopt a holistic approach that encompasses diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes. By understanding how these factors interplay with the GLP-1 mechanism of action, individuals can optimize their treatment outcomes.
Dietary Considerations
A balanced diet rich in nutrients is essential for maximizing GLP-1 effectiveness. Focus on consuming:
- Plenty of vegetables and fruits
- Lean proteins
- Whole grains
- Healthy fats
Avoiding high-calorie, high-fat, and high-sugar foods can also help in achieving better results.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular physical activity not only enhances the effects of GLP-1 medications but also improves overall health. Aim for:
- At least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week
- Incorporating strength training exercises twice a week
Medication Adherence Importance
Adhering to the prescribed GLP-1 medication regimen is crucial for achieving optimal results. Missing doses can lead to reduced efficacy and potential side effects.
Lifestyle Factors That Enhance Results
Other lifestyle adjustments can further enhance GLP-1 effectiveness, including:
- Getting adequate sleep
- Managing stress levels
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
By combining these lifestyle modifications with GLP-1 medication, individuals can maximize their therapeutic benefits and improve their overall quality of life.
Monitoring Your GLP-1 Response: What to Track and When
Understanding how your body responds to GLP-1 medications is crucial for achieving optimal results. GLP-1 therapy timeline can vary among individuals, making personalized monitoring essential.
Blood Glucose Monitoring
For individuals using GLP-1 medications for diabetes management, regular blood glucose monitoring is vital. This helps in understanding how the medication is affecting your blood sugar levels. It’s recommended to track your glucose levels at different times of the day, especially before and after meals.
Weight Tracking Guidelines
If you’re using GLP-1 medications for weight loss, consistent weight tracking is important. Weigh yourself weekly at the same time of day to monitor progress. This data will help you and your healthcare provider adjust your treatment plan as needed.
Symptom and Side Effect Journals
Keeping a journal of any symptoms or side effects can provide valuable insights into how your body is responding to GLP-1 therapy. Note the severity and duration of any side effects, as well as any changes in your overall health.
When to Consult Your Healthcare Provider
Regular consultations with your healthcare provider are crucial for interpreting the data you’ve collected. They can help adjust your treatment plan, address any concerns, and ensure you’re on track to meet your health goals.
By closely monitoring your response to GLP-1 therapy and maintaining open communication with your healthcare provider, you can optimize your treatment outcomes and achieve a better quality of life.
Combining GLP-1 with Other Treatments: Timeline Considerations
The use of GLP-1 medications in combination with other treatments requires careful consideration of timing and potential interactions. GLP-1 receptor agonists are increasingly being used alongside other therapies to manage diabetes and obesity effectively.
GLP-1 with Insulin
Combining GLP-1 receptor agonists with insulin therapy can enhance glycemic control. Studies have shown that this combination can lead to significant improvements in HbA1c levels. However, it’s crucial to monitor for potential hypoglycemia and adjust insulin doses accordingly.
A study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism found that “the addition of a GLP-1 receptor agonist to insulin therapy resulted in improved glycemic control without increasing the risk of severe hypoglycemia.”
“The combination of GLP-1 RA with insulin is a promising therapeutic strategy for patients with type 2 diabetes, offering improved glycemic control and potential weight benefits.”
| Treatment Combination | Effect on HbA1c | Effect on Weight |
|---|---|---|
| GLP-1 + Insulin | Significant reduction | Weight loss or neutrality |
| GLP-1 + Oral Diabetes Medications | Moderate reduction | Weight loss |
GLP-1 with Oral Diabetes Medications
GLP-1 receptor agonists can be effectively combined with oral diabetes medications to improve glycemic control. This combination is particularly beneficial for patients who require additional glucose-lowering effects beyond what oral medications can provide alone.
GLP-1 as Part of Comprehensive Weight Management
For weight management, GLP-1 medications are often used as part of a comprehensive plan that includes diet and exercise. The timeline for weight loss can vary, but significant reductions are typically observed within the first few months of treatment.
Potential Interaction Effects on Timeline
When combining GLP-1 medications with other treatments, it’s essential to consider potential interaction effects that could impact the timeline of therapeutic response. Monitoring for side effects and adjusting treatment plans as needed is crucial.
Key Considerations:
- Monitor blood glucose levels closely when combining GLP-1 with insulin or oral diabetes medications.
- Adjust doses as necessary to minimize the risk of hypoglycemia.
- Regularly review weight and glycemic control to assess the effectiveness of the combination therapy.
Conclusion
GLP-1 agonists offer a powerful tool for weight loss and diabetes management. The effectiveness of these medications depends on various factors, including genetics, metabolism, and baseline weight. A balanced diet and regular exercise significantly enhance results.
Consulting with a healthcare professional ensures a tailored approach, optimizing both safety and effectiveness for long-term success. Weight loss with GLP-1 agonists typically occurs in three distinct phases. For more detailed information on the timeline of GLP-1 medications, you can visit this resource.
To answer the question of how long does it take for GLP-1 to work, it’s essential to understand that individual factors influence outcomes. Generally, significant weight loss and improved diabetes management can be expected within the first few months of treatment.
By understanding the timeline and factors that influence the effectiveness of GLP-1 medications, individuals can better manage their expectations and achieve the best possible outcomes.